Ecological effects of trace metals as limiting/co-limiting micronutrients
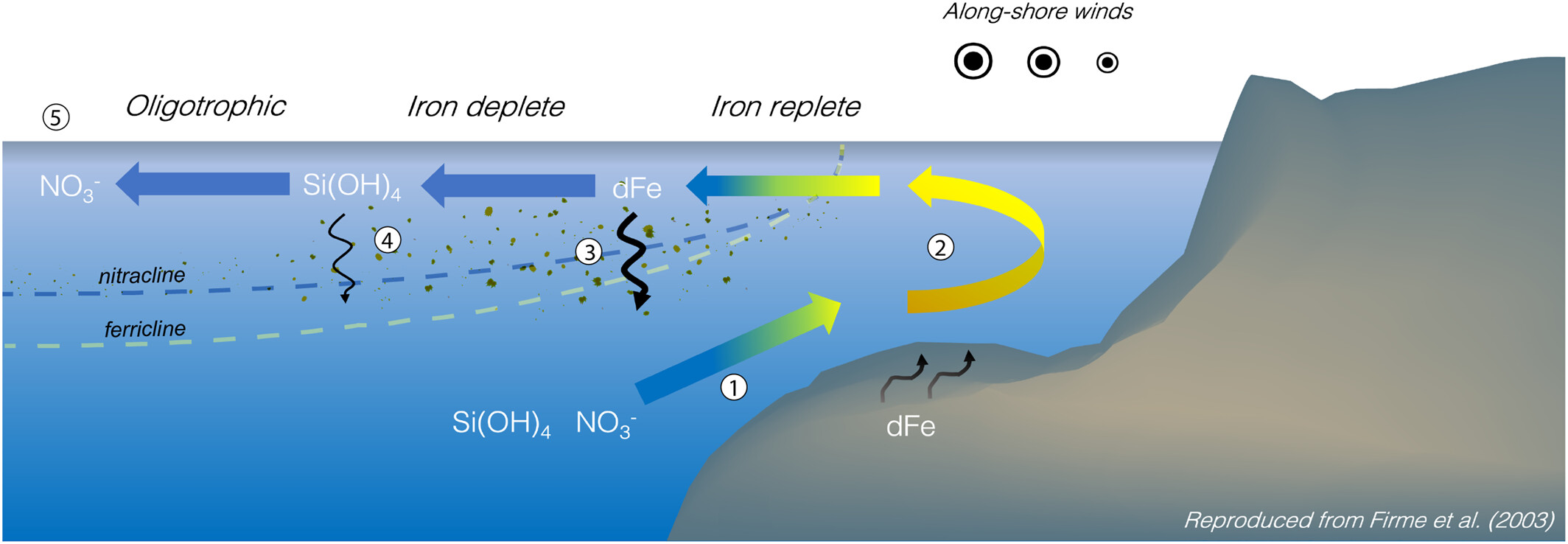
Our group has made progress in demonstrating the ecological significance of Fe availability in oceanic regimes where Fe limitation has not traditionally been thought to occur. One example of this is our work on Fe limitation in the Southern California Current System, a mesotrophic, relatively low-nutrient weak upwelling regime. Our incubation studies and measurements of Fe concentrations have provided evidence that while phytoplankton biomass in this regime is generally limited by the supply of nitrate, Fe supply influences macronutrient utilization, phytoplankton community species composition, and the spatial and temporal distribution of phytoplankton biomass, both at the surface and in the subsurface chlorophyll maximum. Our studies of iron biogeochemistry in this region have been funded by NASA, NSF-OCE and are ongoing as part of the NSF-funded California Current Ecosystem Long Term Ecological Research (CCE-LTER) site. We have also participated in studies of iron limitation around the Antarctic peninsula, in a region of natural iron fertilization.
Recent publications
- Manck, L. E., Coale, T. H., Stephens, B. M., Forsch, K. O., Aluwihare, L. I., Dupont, C. L., Allen, A. E., & Barbeau, K. A. (2024). Iron limitation of heterotrophic bacteria in the California Current System tracks relative availability of organic carbon and iron. The ISME Journal, 18(1), wrae061. doi: 10.1093/ismejo/wrae061.
- Forsch, K. O., Fulton, K. C., Weiss, M. M., Krause, J. W., Stukel, M. R., & Barbeau, K. A. (2023). Iron Limitation and Biogeochemical Effects in Southern California Current Coastal Upwelling Filaments. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 128(11), e2023JC019961. doi: 10.1029/2023JC019961.
-
Forsch, K. O., Hahn-Woernle, L., Sherrell, R. M., Roccanova, V. J., Bu, K. X., Burdige, D., Vernet, M., & Barbeau, K. A. (2021). Seasonal dispersal of fjord meltwaters as an important source of iron and manganese to coastal Antarctic phytoplankton. Biogeosciences, 18(23), 6349–6375. doi: 10.5194/bg-18-6349-2021.
Trace metal speciation in seawater
Recent publications
- Moore, L. E., Heller, M. I., Barbeau, K. A., Moffett, J. W., & Bundy, R. M. (2021). Organic complexation of iron by strong ligands and siderophores in the eastern tropical North Pacific oxygen deficient zone. Marine Chemistry, 236(104021).
doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2021.104021. -
Ruacho, A., Bundy, R. M., Till, C. P., Roshan, S., Wu, J. F., & Barbeau, K. A. (2020). Organic dissolved copper speciation across the US GEOTRACES equatorial Pacific zonal transect GP16. Marine Chemistry, 225(103841). doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2020.103841.
Acquisition and transformation of trace metals by marine microorganisms
Knowledge of the genomic sequences of individual marine microbes as well as access to marine metagenomic data sets has greatly expanded in the last decade. This provides new opportunities to use this information to gain insight into fundamental biogeochemical processes in the ocean, including issues related to trace element cycling. With its strengths in the area of marine molecular biology, SIO is an ideal place to pursue these interests. An example of the application of genomics and molecular biology to studies of trace metal cycling in the marine environment is our work on receptor-mediated heme acquisition by marine bacteria. Uptake of exogenous heme complexes is a novel microbial Fe scavenging strategy in the context of marine systems, which has been identified by the Barbeau group. This project involves computational genomic studies, as well as gene expression studies and laboratory experiments with model bacterial strains. Our ongoing efforts in this area seek to combine genomic information and molecular biology techniques with chemical measurements and experimentation to increase our understanding of Fe speciation and transformation in the ocean. We work with a variety of model marine bacteria strains in culture, including ecologically significant heterotrophs and cyanobacteria like Trichodesmium. Our work in this area has been funded by NSF and also the ACS Petroleum Research Fund.

Recent publications
- Stow, P. R., Forsch, K. O., Thomsen, E., Naka, H., Haygood, M. G., Barbeau, K. A., & Butler, A. (2025). Stereospecific control of microbial growth by a combinatoric suite of chiral siderophores. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 122(10), e2423730122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2423730122.
- Lampe, R. H., Coale, T. H., Forsch, K. O., Jabre, L. J., Kekuewa, S., Bertrand, E. M., Horák, A., Oborník, M., Rabines, A. J., Rowland, E., Zheng, H., Andersson, A. J., Barbeau, K. A., & Allen, A. E. (2023). Short-term acidification promotes diverse iron acquisition and conservation mechanisms in upwelling-associated phytoplankton. Nature Communications, 14(1), 7215. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42949-1.
- Manck, L. E., Park, J., Tully, B. J., Poire, A. M., Bundy, R. M., Dupont, C. L., & Barbeau, K. A. (2021). Petrobactin, a siderophore produced by Alteromonas, mediates community iron acquisition in the global ocean. Isme Journal, 12. doi: 10.1038/s41396-021-01065-y.
-
Manck, L. E., Espinoza, J. L., Dupont, C. L., & Barbeau, K. A. (2020). Transcriptomic study of substrate-specific transport mechanisms for iron and carbon in the marine copiotroph Alteromonas macleodii. MSystems, 5(2). doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00070-20.
